Extractions
The main goal of dentistry is to preserve your natural teeth and keep them healthy for as long as possible. There are times, however, when it is in your best interest (or your child’s) to have a tooth extracted (removed). This could be the case for a variety of reasons. Perhaps you have a tooth that has been severely damaged by trauma or decay; or an impacted wisdom tooth that may cause trouble for you later on. Maybe your teenager will soon undergo orthodontic treatment and has insignificant space for his adult teeth, referred to as crowding. Or your younger child has a baby tooth that’s stubbornly adhering, even though it’s past time for it to go.
Whatever the reason, tooth extraction is more often than not a very routine procedure. How straightforward this minor surgery is will depend on where the tooth to be extracted is located in the mouth, and what its roots are like. For example, a front tooth with a single straight root is easier to remove than a molar with multiple roots. This is especially true when that molar is a wisdom tooth that is impacted, meaning it is below the surface surrounded by gum tissue and bone. Often, a wisdom tooth is blocked from fully erupting (growing in) by other teeth in its path.
Still, tooth extraction is nothing to be feared when done by an experienced hand. Keep in mind that a tooth is not rigidly fixed in its surrounding bone, though that’s how some may picture it. In fact, it is attached to the bone via a network of fibers that form what’s known as the periodontal ligament. By carefully manipulating the tooth, these fibers can be detached and the tooth freed without much trouble.
Reasons for Extracting a Tooth
As mentioned above, there can be a variety of reasons for extracting a tooth. Be sure to ask questions about the pros and cons of any dental treatment, including extraction.
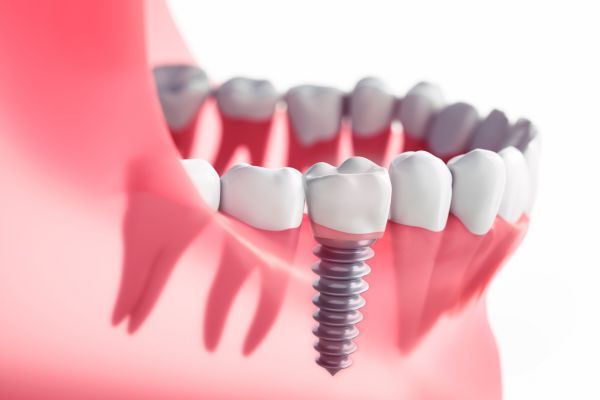
- Trauma or Disease — In both of these situations, there are several ways to try and save the tooth. The damaged tooth might need a full-coverage crown, a root canal treatment, or both. But sometimes even these methods are not enough to keep the tooth functioning well and looking good; it might be better to remove the tooth and replace it with a strong and lifelike dental implant.
- Orthodontic Treatment — Teeth are sometimes extracted when there are too many of them for the size of the dental arches (jaws), a situation known as crowding. After an adequate amount of space is opened up through the extraction of one or more teeth, the remaining teeth can be aligned properly. The teeth most frequently removed for orthodontic reasons are the first premolars, which are right next to the eyeteeth (canines).
- Impacted Wisdom Teeth — Early removal of impacted wisdom teeth can prevent damage to neighboring healthy teeth, bone, gum tissue, even nerves and blood vessels. If an impacted wisdom tooth is in a bad position, it’s best to remove it before its roots are fully formed.
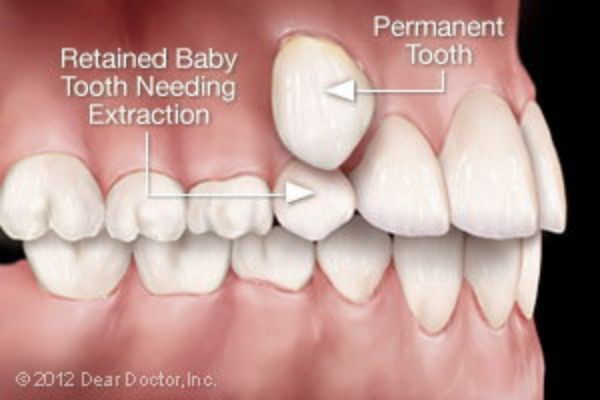
- Baby Teeth — If a baby tooth is out of position or not lost in the right sequence, the permanent tooth underneath it might not erupt normally. In this case, removing the baby tooth could prevent a need for orthodontic treatment later on.
The Process of Extracting a Tooth
The first step in any extraction is a radiographic (x-ray) examination to assess the position of the tooth roots and the condition of the surrounding bone. This will allow any possible complications to be anticipated. A thorough medical and drug history is taken, to ensure that you are healthy enough to undergo the procedure, and your options for anesthesia will be discussed.
Tooth extraction is usually carried out with local anesthesia, which will numb the teeth to be removed, and the surrounding bone and gum tissues. Additional sedatives might also be used, including oral sedatives (taken in pill form), nitrous oxide (which is inhaled) and/or conscious sedation, which is given intravenously (into a vein). The latter is usually required for more complicated (or multiple) tooth extractions. By the time the sedation medication has worn off, you won’t even be aware that the surgery was done.
As your tooth is being removed, steps are taken to ensure the bone that surrounds it isn’t damaged. Sometimes, in the process of removing a tooth, a small amount of lab-processed bone-grafting material is placed into the socket to help preserve the bone volume there. This is particularly important when the extraction is going to be followed at some point by the placement of a dental implant, which needs to fuse to existing bone, or orthodontics, which gently moves teeth through bone.
What to Expect After Tooth Extraction
Immediately after your tooth is extracted, the socket will be covered with sterile gauze; gentle pressure will be applied for 10-20 minutes to control any bleeding. Small sutures (stitches) might also be used for this purpose. It’s normal to experience some mild to moderate post-operative discomfort and/or swelling. Taking non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and/or aspirin the day of surgery should control most symptoms. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to ensure infection-free healing. Using ice packs on the outside of your jaw, and eating softer foods until you feel more comfortable can also be helpful. Within a few days, all should be back to normal.