Crowns & Bridgework
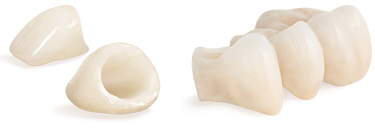 Dentistry is an art as well as a science; dental crowns offer a perfect example of this. A dental crown or “cap” is a covering that fits over a damaged, decayed or unattractive tooth. It can even replace a tooth entirely as part of dental bridgework.
Dentistry is an art as well as a science; dental crowns offer a perfect example of this. A dental crown or “cap” is a covering that fits over a damaged, decayed or unattractive tooth. It can even replace a tooth entirely as part of dental bridgework.
A crown completely covers a tooth above the gum line. This is in contrast to a dental veneer, which only covers a tooth’s front surface and needs natural tooth structure to support it. Therefore, if a tooth is missing a significant amount of structure above the gum line, a crown would be the restoration of choice.
Crowns strengthen damaged teeth, allowing them to function normally again. When crafted from today’s high-tech porcelains (dental ceramics), crowns are virtually indistinguishable from natural teeth. They can even be designed to improve upon a tooth’s original appearance.
There are other materials besides porcelain that we can use to make dental crowns, depending on what qualities are most important. For durability, cast gold can’t be beat. However, this is not always the most aesthetic choice — especially towards the front of the mouth. Other possibilities include porcelain-fused-to-metal crowns (PFM), which have a metal interior for strength and a porcelain exterior for a more natural appearance, and all-porcelain crowns with zirconia, representing the strongest ceramic. We would be happy to discuss the pros and cons of these various options with you.

Crowning or Capping a Tooth
Crowning or capping a tooth will usually take two to three visits. At the first visit, your tooth is prepared to receive its new crown. First, it is shaped to fit inside the new covering. This will involve some drilling to give the tooth a uniform shape. The tooth and the surrounding area will be numbed beforehand. If there is very little tooth structure left to begin with, the tooth may have to be built up with filling material, rather than filed down, to support the crown.
After the tooth is prepared, impressions of your teeth are taken, either digitally or with reliable, putty-like impression materials, and sent to the dental laboratory. There, the impressions will be used to make models of your teeth for the creation of a crown. The models will serve as guides to the highly skilled lab technicians, who will ensure that your new crown is designed to enhance your smile and function well within your bite.
Before you leave the office, a temporary crown will be attached to your tooth to protect it until the permanent crown is ready. At the second visit, your permanent crown will be attached to your tooth with either aresin that hardens when exposed to a special light source, or a type of permanent cement.
 Creating a Bridge
Creating a Bridge
Crowns can also be used to create a lifelike replacement for a missing tooth. This is done with bridgework, which spans the space of the missing tooth and requires at least three crowns. Two of those crowns will be placed over healthy teeth on either side of the missing tooth; these healthy teeth are referred to as abutment teeth. The two crowned abutment teeth become supports for a third crown placed in between them; that third crown is referred to as a pontic. If more than one tooth is missing, more crowns will be needed to bridge the gap in between the abutment teeth.
The number of abutment teeth necessary to replace missing teeth is influenced by the number of missing teeth, the size and length of the abutment tooth roots, the amount of bone support each abutment tooth has, as well as where in the mouth the missing tooth is located. For example, if you have three missing teeth, four abutment teeth may be necessary, thereby creating a seven-tooth bridge. Engineering and designing of the bridge requires an understanding of how to replace teeth, as well as the biology of the supporting gum and bone tissue.
Caring for Your Crowns & Bridgework
Crowns and bridgework require the same conscientious care as your natural teeth. Be sure to brush and floss between all of your teeth — restored and natural — every day to reduce the buildup of dental plaque. When you have crowns, it is even more important to maintain your regular schedule of cleanings at the dental office. Avoid using your teeth as tools (to open packages, for example). If you have a grinding habit, wearing a nightguard would be a good idea to protect your teeth and your investment.











 Most often, bad breath originates in the mouth, from trapped food particles that are then processed by oral bacteria. The most common location for mouth-related bad breath is the back of the tongue, where large quantities of naturally occurring bacteria can thrive on food remnants, dead skin cells and post-nasal drip (mucus coming down your throat from the nose). The waste products of these bacteria include volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs), which have a smell resembling rotten eggs. Other places where bacteria and food particles can be trapped are between the teeth, beneath the gums, and in oral appliances or dentures. Poor oral hygiene sets the stage for these problems, as well as for tooth decay and gum disease, which can also cause foul odors.
Most often, bad breath originates in the mouth, from trapped food particles that are then processed by oral bacteria. The most common location for mouth-related bad breath is the back of the tongue, where large quantities of naturally occurring bacteria can thrive on food remnants, dead skin cells and post-nasal drip (mucus coming down your throat from the nose). The waste products of these bacteria include volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs), which have a smell resembling rotten eggs. Other places where bacteria and food particles can be trapped are between the teeth, beneath the gums, and in oral appliances or dentures. Poor oral hygiene sets the stage for these problems, as well as for tooth decay and gum disease, which can also cause foul odors.
 Most of the lumps, bumps, and occasional sores you find in and around your mouth are completely harmless. But you should look out for changes such as white or red patches, ulcers and lumps anywhere in and around your face and neck that persist for more than a couple of weeks. A persistent sore throat or hoarseness is also cause for concern. Most oral cancers are “squamous” (scale-shaped) cell carcinomas. The sides of the tongue are the most common sites for these small lesions. Because the tongue has a rich blood supply and a direct connection to the lymphatic system (a part of our immune system), it’s a site from which cancer can easily spread. The floor of the mouth under the tongue is the second most common site. Cancerous lesions on the lower lip, which are usually preceded by chronic sun exposure, are not uncommon.
Most of the lumps, bumps, and occasional sores you find in and around your mouth are completely harmless. But you should look out for changes such as white or red patches, ulcers and lumps anywhere in and around your face and neck that persist for more than a couple of weeks. A persistent sore throat or hoarseness is also cause for concern. Most oral cancers are “squamous” (scale-shaped) cell carcinomas. The sides of the tongue are the most common sites for these small lesions. Because the tongue has a rich blood supply and a direct connection to the lymphatic system (a part of our immune system), it’s a site from which cancer can easily spread. The floor of the mouth under the tongue is the second most common site. Cancerous lesions on the lower lip, which are usually preceded by chronic sun exposure, are not uncommon.



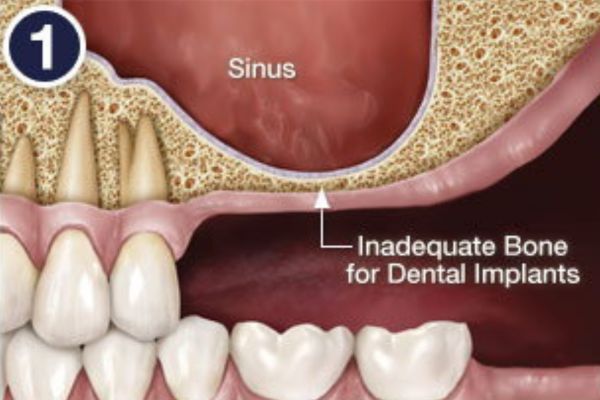
 A sinus membrane lift, or sinus augmentation, involves adding bone to fill in the bottom of that air space, essentially raising the floor of the sinus cavity. Why wouldn’t there be enough bone there already? For some people, it’s simply a matter of how large their sinus cavities are, and their shape. In other cases, bone has actually been lost from the area. For example, if your tooth has been missing a long time, the bone that used to surround it may have begun to deteriorate. Bone in general needs stimulation to stay strong; in the case of the jawbone, that stimulation comes from the teeth. When teeth are lost, the bone loses stimulation and the body ceases to make new bone cells in that area. This leads to a reduction in bone volume and density. Also, if your tooth loss was due to periodontal (gum) disease, your tooth-supporting bone may have been reduced as a result of the disease. No matter what the reason is for insufficient bone, a sinus membrane lift can create more bone where it is needed.
A sinus membrane lift, or sinus augmentation, involves adding bone to fill in the bottom of that air space, essentially raising the floor of the sinus cavity. Why wouldn’t there be enough bone there already? For some people, it’s simply a matter of how large their sinus cavities are, and their shape. In other cases, bone has actually been lost from the area. For example, if your tooth has been missing a long time, the bone that used to surround it may have begun to deteriorate. Bone in general needs stimulation to stay strong; in the case of the jawbone, that stimulation comes from the teeth. When teeth are lost, the bone loses stimulation and the body ceases to make new bone cells in that area. This leads to a reduction in bone volume and density. Also, if your tooth loss was due to periodontal (gum) disease, your tooth-supporting bone may have been reduced as a result of the disease. No matter what the reason is for insufficient bone, a sinus membrane lift can create more bone where it is needed.

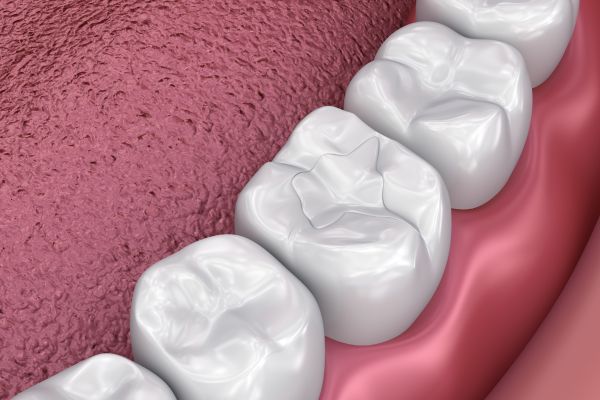
 If you have never had a cavity, congratulations! If you have had one, you are not alone. About 78% of us have had at least one cavity by the time we reach age 17, according to a 2000 report by the U.S. Surgeon General. Fortunately there’s a time-tested treatment for cavities: the dental filling.
If you have never had a cavity, congratulations! If you have had one, you are not alone. About 78% of us have had at least one cavity by the time we reach age 17, according to a 2000 report by the U.S. Surgeon General. Fortunately there’s a time-tested treatment for cavities: the dental filling.


