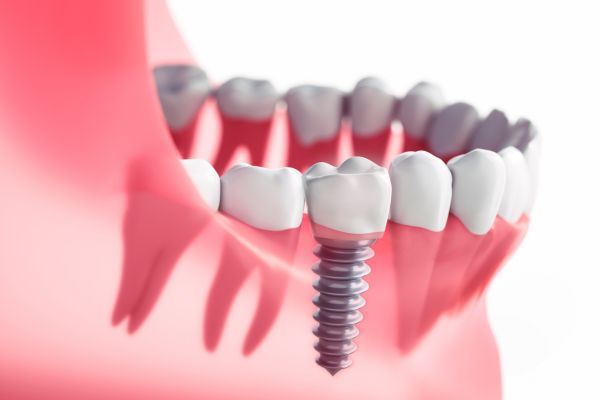
The dental implant is today’s state-of-the-art tooth replacement method. It consists of a very small titanium post (the actual implant), which is attached to a lifelike dental crown. The crown is the only part of this tooth-replacement system that is visible in your mouth. The implant itself rests beneath your gum line in the bony socket that used to hold your missing tooth. Two, four or more implants can be used to support multiple crowns, or even an entire arch of upper or lower replacement teeth. Whether you are missing one tooth, several teeth or all your teeth, dental implants are preferred by doctors and patients alike. That’s because dental implants are:
Most Like Natural Teeth
Your natural teeth have roots that keep them securely anchored to your jawbone. In a similar way, implant teeth form a solid attachment with the bone in your jaw. This is possible because dental implants are made of titanium, a metal that has a unique ability to fuse to living bone. After an implant is inserted during a minor procedure done in the dental office, it will become solidly fused to your bone over a period of several months. Once that happens, your implant-supported replacement tooth (or teeth) will feel completely natural. It will also be visually indistinguishable from your natural teeth. Implant teeth allow you to eat, speak and smile with complete confidence because they will never slip or shift like removable dentures often do.
The Longest-Lasting Tooth Replacements
Because dental implants actually become part of your jawbone, they provide a permanent solution to tooth loss. Whereas other methods of tooth replacement, including removable dentures and bridgework, may need to be replaced or remade over time, properly cared-for dental implants should last a lifetime. That’s what makes this choice of tooth replacement the best long-term value.
Able To Prevent Bone Loss
You may not know it, but bone loss inevitably follows tooth loss. Bone is a living tissue that needs constant stimulation to rebuild itself and stay healthy. In the case of your jawbone, that stimulation comes from the teeth. When even one tooth is lost, the bone beneath it begins to resorb, or melt away. This can give your face a prematurely aged appearance and even leave your jaw more vulnerable to fractures if left untreated long enough (View Example). Dental implants halt this process by fusing to the jawbone and stabilizing it. No other tooth replacement method can offer this advantage.
Safe For Adjacent Natural Teeth
Dental implants have no effect on the health of adjacent natural teeth; other tooth-replacement systems, however, can weaken adjacent teeth. With bridgework, for example, the natural teeth on either side of a gap left by a missing tooth must provide support for the dental bridge. This can stress those adjacent teeth and leave them more susceptible to decay. Likewise, a partial denture relies on adjacent natural teeth for support and may cause those teeth to loosen over time. Dental implants are stand-alone tooth replacements that don’t rely on support from adjacent natural teeth.
Easy To Care For
Caring for implant teeth is no different than caring for your natural teeth. You must brush them and floss them daily. But you’ll never have to apply special creams and adhesives, or soak them in a glass overnight, as you would with dentures. They’ll also never need a filling or a root canal, as the natural teeth supporting bridgework might. While implants can never decay, they can be compromised by gum disease. Good oral hygiene and regular visits to the dental office for professional cleanings and exams is the best way to prevent gum disease, and to ensure your dental implants last a lifetime, as they’re designed to do.
Two Types of Periodontal Disease
Gingivitis is a chronic bacterial infection. It occurs when plaque builds up around a tooth and creates a sticky layer which causes inflammation of the gum tissue. You may see redness, swelling and bleeding of the gum around your tooth.
Periodontitis is also a chronic bacterial infection. It occurs in susceptible patients when a long-term gum infection is not treated. Infection and resultant inflammation lead to the loss of ligaments and bone around the root of your tooth making a deep pocket. Factors which significantly increase the risk of developing periodontitis include:
- Genetics
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Medications (certain anti-seizure, blood pressure, and immunosuppressant medications)
- Stress
- Poor Oral Hygiene
Prophy/cleanings
Prophy appointments help prevent or reverse gingivitis, (infection and inflammation of the gums around the neck of the tooth), by removing plaque and mineralized plaque or tartar/calculus on the teeth. A Prophy is typically recommended every six months to help keep you healthy.
Periodontal maintenance
Periodontal maintenance appointments take the place of a prophy after you have had treatment for periodontitis, (infection that deteriorates the gums and bone around the root of the tooth). These appointments can be more frequent than a regular prophy to help keep periodontitis stable. These maintenance visits disrupt disease causing bacteria below the gumline by removing plaque and tarter above and below the gumline.
Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy
The goal of non-surgical periodontal therapy is to stop active infection and establish a healthy environment below the gumline. Your hygienist does this by removing tartar/calculus in the periodontal pocket which reduces the microbial load and toxins. It may require more than one appointment.
Materials used during Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy
The following materials and techniques may be used in your nonsurgical periodontal therapy:
- Hand held instruments known as scalers and ultrasonics to clean the teeth.
- Local anesthetic (numbing) to control sensitivity.
- Antibacterial rinses to help decrease plaque and calculus.
- Antibiotic pills to help kill bacteria and viruses and reduce the destructive response some people have to periodontal infections.
- Laser treatment to control bacterial levels around affected areas.
Benefits of Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy
Some potential benefits of non-surgical periodontal therapy include:
- Eliminating the infection present
- Controlling further infections and bone loss
- Reducing swollen and bleeding gums
- Reducing bad breath
- Avoiding tooth loss
- Decreasing the risk for diseases associated with periodontal disease such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis
- Decreasing the risk of preterm low birth weight babies in pregnant women
Health Implications of Deep Dental Pockets
While tooth loss is typically the biggest concern associated with periodontal pockets, the infection poses a significant risk to your overall health. Active gum disease drastically increases the risk and severity of systemic health conditions like:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Infertility
- Erectile dysfunction
- Preeclampsia
- Pneumonia
- Respiratory illness
- Alzheimer’s Disease (possibly)
Seeing a dentist for periodontal treatment isn’t just important for your smile, it’s vital to your health.
 The most likely location for a cavity to develop in your child’s mouth is on the chewing surfaces of the back teeth. Run your tongue over this area in your mouth, and you will feel the reason why: These surfaces are not smooth, as other areas of your teeth are. Instead, they are filled with tiny grooves referred to as “pits and fissures,” which trap bacteria and food particles. The bristles on a toothbrush can’t always reach all the way into these dark, moist little crevices. This creates the perfect conditions for tooth decay.
The most likely location for a cavity to develop in your child’s mouth is on the chewing surfaces of the back teeth. Run your tongue over this area in your mouth, and you will feel the reason why: These surfaces are not smooth, as other areas of your teeth are. Instead, they are filled with tiny grooves referred to as “pits and fissures,” which trap bacteria and food particles. The bristles on a toothbrush can’t always reach all the way into these dark, moist little crevices. This creates the perfect conditions for tooth decay.










 Who’s At Risk for Developing Oral Cancer?
Who’s At Risk for Developing Oral Cancer? A thorough screening for oral cancer is part of your routine dental checkup — another reason why you should be examined regularly. The screening includes a visual assessment of your lips, tongue, and the inside of your mouth, including a check for red or white patches or unusual sores. You may be palpated (pressed with fingers) to detect the presence of lumps and swellings, and your tongue may be gently pulled aside for an even better view. A special light, dye, or other procedure may also be used to help check any suspect areas. If anything appears to be out of the ordinary, a biopsy can be easily performed.
A thorough screening for oral cancer is part of your routine dental checkup — another reason why you should be examined regularly. The screening includes a visual assessment of your lips, tongue, and the inside of your mouth, including a check for red or white patches or unusual sores. You may be palpated (pressed with fingers) to detect the presence of lumps and swellings, and your tongue may be gently pulled aside for an even better view. A special light, dye, or other procedure may also be used to help check any suspect areas. If anything appears to be out of the ordinary, a biopsy can be easily performed.