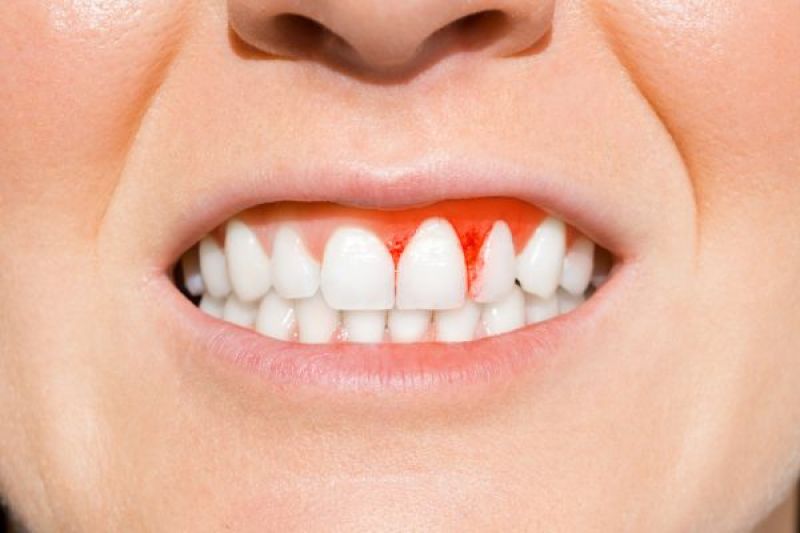
Two Types of Periodontal Disease
Gingivitis is a chronic bacterial infection. It occurs when plaque builds up around a tooth and creates a sticky layer which causes inflammation of the gum tissue. You may see redness, swelling and bleeding of the gum around your tooth.
Periodontitis is also a chronic bacterial infection. It occurs in susceptible patients when a long-term gum infection is not treated. Infection and resultant inflammation lead to the loss of ligaments and bone around the root of your tooth making a deep pocket. Factors which significantly increase the risk of developing periodontitis include:
- Genetics
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Medications (certain anti-seizure, blood pressure, and immunosuppressant medications)
- Stress
- Poor Oral Hygiene
Prophy/cleanings
Prophy appointments help prevent or reverse gingivitis, (infection and inflammation of the gums around the neck of the tooth), by removing plaque and mineralized plaque or tartar/calculus on the teeth. A Prophy is typically recommended every six months to help keep you healthy.
Periodontal maintenance
Periodontal maintenance appointments take the place of a prophy after you have had treatment for periodontitis, (infection that deteriorates the gums and bone around the root of the tooth). These appointments can be more frequent than a regular prophy to help keep periodontitis stable. These maintenance visits disrupt disease causing bacteria below the gumline by removing plaque and tarter above and below the gumline.
Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy
The goal of non-surgical periodontal therapy is to stop active infection and establish a healthy environment below the gumline. Your hygienist does this by removing tartar/calculus in the periodontal pocket which reduces the microbial load and toxins. It may require more than one appointment.
Materials used during Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy
The following materials and techniques may be used in your nonsurgical periodontal therapy:
- Hand held instruments known as scalers and ultrasonics to clean the teeth.
- Local anesthetic (numbing) to control sensitivity.
- Antibacterial rinses to help decrease plaque and calculus.
- Antibiotic pills to help kill bacteria and viruses and reduce the destructive response some people have to periodontal infections.
- Laser treatment to control bacterial levels around affected areas.
Benefits of Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy
Some potential benefits of non-surgical periodontal therapy include:
- Eliminating the infection present
- Controlling further infections and bone loss
- Reducing swollen and bleeding gums
- Reducing bad breath
- Avoiding tooth loss
- Decreasing the risk for diseases associated with periodontal disease such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis
- Decreasing the risk of preterm low birth weight babies in pregnant women
Health Implications of Deep Dental Pockets
While tooth loss is typically the biggest concern associated with periodontal pockets, the infection poses a significant risk to your overall health. Active gum disease drastically increases the risk and severity of systemic health conditions like:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Infertility
- Erectile dysfunction
- Preeclampsia
- Pneumonia
- Respiratory illness
- Alzheimer’s Disease (possibly)
Seeing a dentist for periodontal treatment isn’t just important for your smile, it’s vital to your health.
Table of Contents
More Categories
Other Articles You May Be Interested In