Osteoporosis & Oral Health
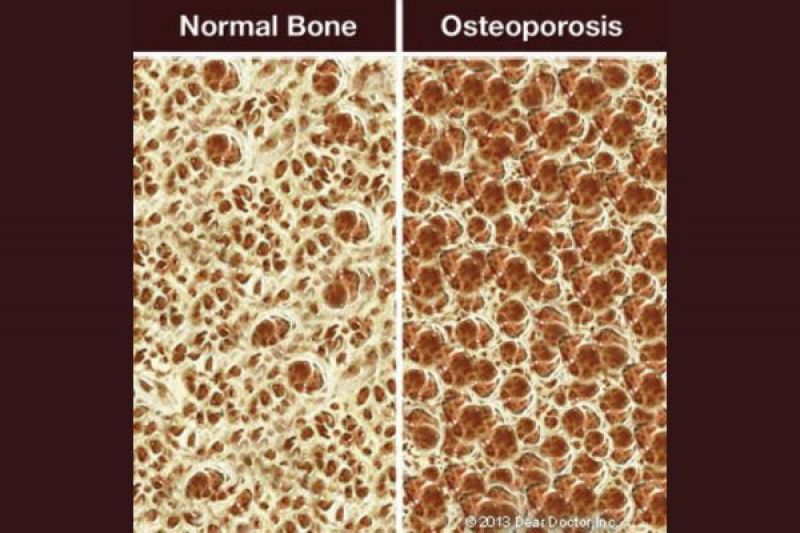
Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones and makes them more prone to fracture. Estimated to affect about 10 million Americans at present, it causes some 2 million fractures each year — and as our population ages, these numbers are expected to increase. Osteoporosis can affect any part of the body — including the jawbone that supports the teeth.
This may be of particular concern if you are considering certain dental procedures — for example, getting dental implants to replace missing teeth. Implants are today’s gold standard for tooth replacement, because they look and function so much like real teeth. But their success depends on a process known as osseointegration, by which they fuse to living bone in the jaw. For this to occur, that bone must be relatively healthy; yet osteoporosis — and certain medications used to treat it — may affect your oral health.
Bone: An Ever-Changing Tissue
The living bone tissue in the body isn’t like the dry, white skeleton you may have seen in a doctor’s office or on TV. It is constantly being remodeled by two natural processes: resorption, in which the body removes and breaks down old, damaged bone; and bone formation, where the removed material is replaced by new, healthy bone. In an ideal situation, both processes happen at an equal rate; osteoporosis, however, tips the balance toward resorption, weakening the bone structure.
A class of drugs called bisphosphonates (whose brand names include Fosamax, Boniva, Reclast and Prolia) can inhibit resorption and help bring the two processes back into balance. But for reasons that aren’t fully understood, these medications sometimes have a different effect on the bones of the jaw. In rare cases, long-term bisphosphonate users experience osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), a condition in which isolated areas of jawbone lose their vitality and die. If you are a candidate for oral surgery, tooth extraction or implant placement, it’s important to consider the possible effect of bisphosphonate use before you have this type of procedure.
Taking Medication
Over 90 percent of the people who suffer from bisphosphonate-associated ONJ received high doses of the medication intravenously — often for cancer treatment. Only a small percentage of those who take the drug orally are likely to develop this condition. So generally speaking, if you have osteoporosis or are at high risk of bone fractures, the benefit of taking these medications far outweighs the risk.
But if you are about to begin therapy with high doses of bisphosphonates, it’s ideal to have a dental exam and resolve any oral disease before beginning the medication. Likewise, while you’re receiving the medication, it’s best to avoid invasive dental treatments if possible. However, since untreated oral disease may cause serious health problems, be sure to discuss the situation with all members of your medical team before making treatment decisions.
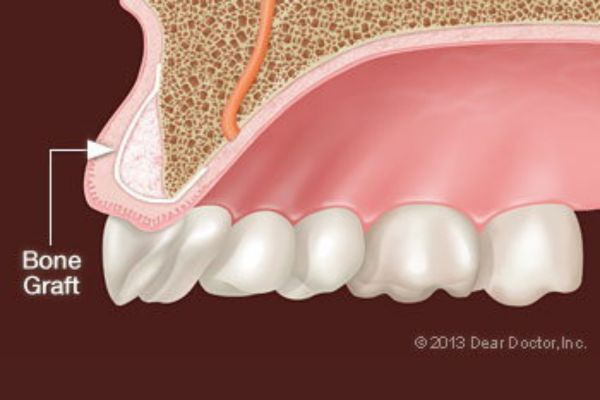
Most people who take oral bisphosphonates for osteoporosis won’t have to postpone or avoid dental procedures, because they have little risk of developing ONJ. In the case of dental implant placement, the decision to proceed is made on an individual basis, after a thorough examination of the quality and quantity of tooth-supporting bone in the jaw. The presence of osteoporosis may influence the type of implants used, and the amount of healing time needed to complete the osseointegration process.
No matter what dental procedures you are considering, it is vital to keep us informed about any medical conditions you have, and any drugs you may be taking — both prescription and non-prescription.
Preventing Osteoporosis
There are several ways you can help prevent osteoporosis. For a start, make sure you’re getting enough calcium and vitamin D. It also helps to decrease your caffeine and alcohol intake, and quit smoking. Weight-bearing exercise — physical activities that force you to work against gravity, like walking, jogging or weight training — can bring a host of benefits. And don’t forget your regular visits to the dental office. Your dental professionals don’t just help you to maintain good oral health — we encourage you to keep up your overall health as well.
Table of Contents
More Categories
Other Articles You May Be Interested In